Integrating wearable telemetry to shorten athlete downtime
Wearable telemetry can help reduce athlete downtime by delivering continuous data on movement, workload, and recovery. This article explains practical integration steps, the role of biomechanics and nutrition data, and how teams can use wearables to support conditioning and rehabilitation.
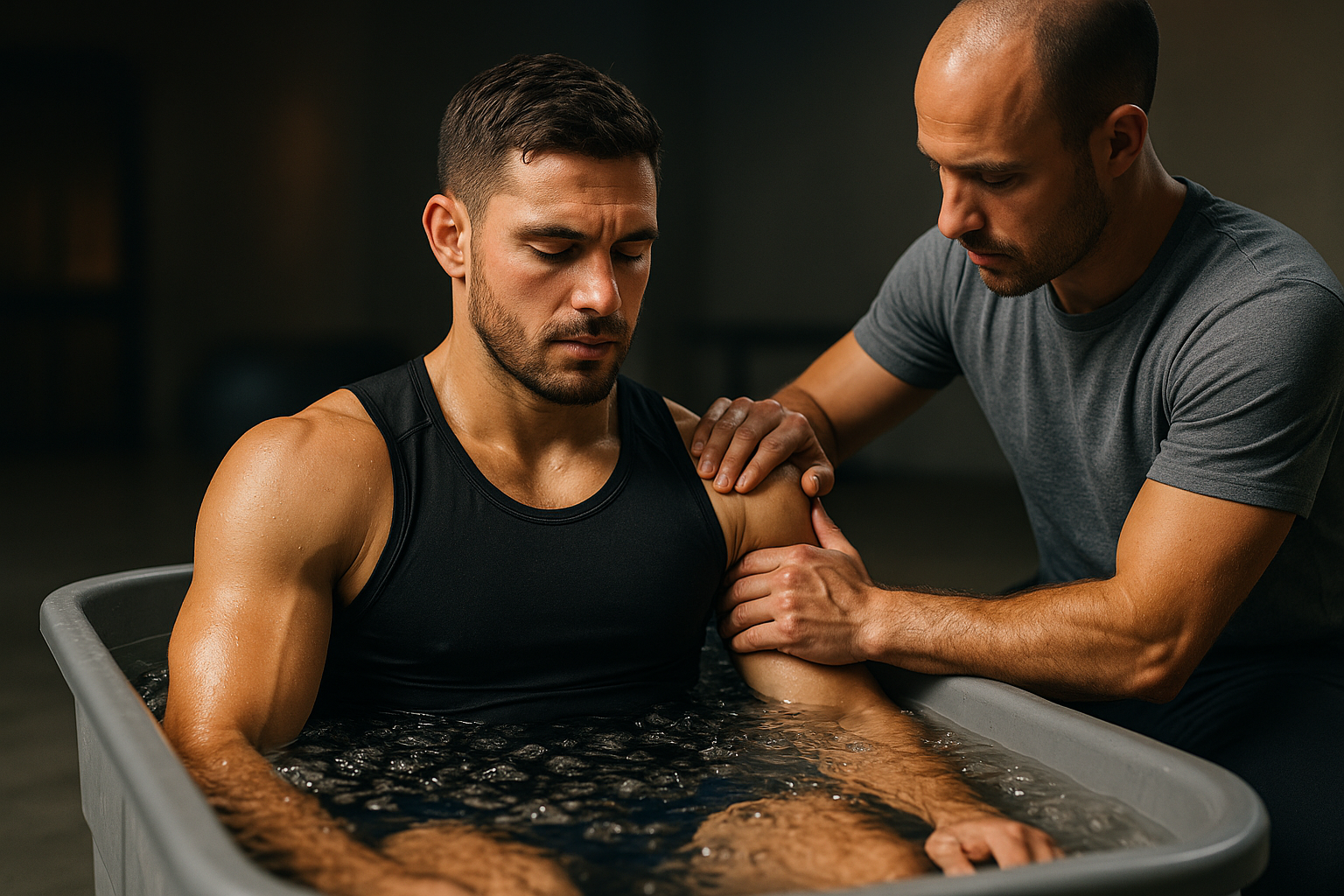

Athletes and their support teams increasingly rely on wearable telemetry to make data-driven decisions that reduce downtime after injury or intense training. By combining continuous sensor data with structured screening and individualized conditioning plans, practitioners can monitor workload, detect early signs of excessive strain, and adapt rehabilitation protocols. Integrating telemetry requires attention to data quality, battery life, and durability of devices, plus workflows that translate metrics into actionable plans for strength, mobility, and recovery. This article outlines practical approaches for deploying wearables across screening, loadmanagement, conditioning, and rehabilitation pathways.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
How do wearables support screening and durability?
Wearables extend pre-season and return-to-play screening by providing objective measures beyond clinical tests. Accelerometers, gyroscopes, and heart-rate sensors can capture movement symmetry, impact exposure, and physiological stress during drills. Screening with wearables helps identify athletes at higher risk from persistent asymmetries or mechanical inefficiencies, and device durability matters when sensors withstand repeated sessions and environmental exposure. Reliable hardware and consistent placement protocols improve data quality, which makes longitudinal comparisons during conditioning and rehabilitation more meaningful.
How can telemetry guide loadmanagement and workload?
Telemetry enables granular tracking of workload both within sessions and across microcycles. External load (accelerations, sprint distance) and internal load (heart rate variability, perceived exertion proxies) are combined to inform loadmanagement strategies. Teams can set progressive loading curves that reduce sudden spikes in workload linked to injury risk, and use telemetry to adjust training density or recovery days. Consistent telemetry patterns allow the athlete and coach to balance adaptation with recovery, reducing unnecessary downtime caused by overuse.
Where do biomechanics and conditioning intersect?
Biomechanics data from wearables helps tailor conditioning by revealing movement patterns that limit performance or predispose to injury. Joint-angle estimates, landing mechanics, and acceleration profiles inform targeted strength and mobility work. Conditioning programs that integrate biomechanical feedback can address specific deficits—such as weak hip control or poor deceleration technique—so that strength and mobility gains translate into safer sport-specific movements. Embedding these metrics into regular sessions accelerates the feedback loop between training and measurable movement improvements.
How do wearables track strength, mobility, and recovery?
Wearable telemetry can quantify explosive power, asymmetry in single-leg tasks, and range-of-motion proxies during standard assessments. Combining these outputs with self-reported recovery and sleep metrics provides a multidimensional view of readiness. When strength or mobility gains plateau or regress, telemetry trends help clinicians adjust rehabilitation load, modify exercises, or introduce additional recovery strategies. Regular objective tracking of these variables shortens the time to identify setbacks and allows faster, evidence-informed adjustments to interventions.
How does telemetry inform rehabilitation and nutrition?
During rehabilitation, telemetry helps calibrate progression by measuring movement quality under increasing loads. Objective thresholds can determine when to advance from isolated strength tasks to sport-specific conditioning. Nutrition data, collected as logs or via integration with diet tracking apps, complements telemetry by revealing recovery windows and fueling needs tied to workload. Combining telemetry trends with nutrition and sleep data supports a holistic rehab plan focused on restoring endurance and tissue durability while minimizing reinjury risk.
Integrating telemetry for endurance, durability, and recovery
Successful integration requires workflows that convert raw telemetry into concise insights for coaches, clinicians, and athletes. Standardize data collection times (screening, post-training, rehab milestones), ensure device calibration and consistent sensor placement, and define actionable thresholds for endurance, durability, and recovery metrics. Cross-disciplinary review meetings that include conditioning, rehabilitation, and nutrition staff help interpret the data and align adjustments. Prioritizing athlete data privacy and choosing devices with sufficient battery life and durability will maintain consistent monitoring and reduce gaps that can prolong downtime.
In summary, wearable telemetry offers a pathway to shorten athlete downtime by enabling earlier detection of risk, more precise loadmanagement, and targeted conditioning and rehabilitation. When devices are reliable and integrated into multidisciplinary workflows, telemetry becomes a practical tool to optimize strength, mobility, endurance, and recovery while supporting safer returns to sport.